The goal of urban active fault detection is to accurately understand the spatial distribution of active faults in the city, the risk of strong earthquakes and the background of deep-seated seismicity, and to take effective preventive measures based on this information, so as to mitigate the losses caused by potential seismic hazards.
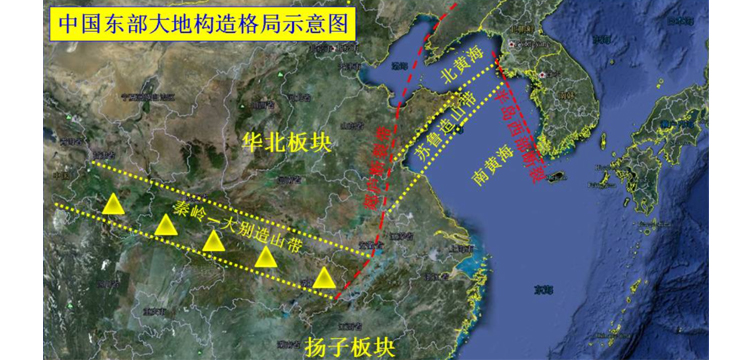
The Tanlu Fracture Zone is the largest seismically active zone in eastern China. Mingguang City, Anhui Province, is located in the junction of the middle and southern sections of the Tantanlu Fracture Zone, where the study of the site response characteristics, structure and detection of active faults is of great scientific value and practical significance for disaster mitigation and prevention.
Active fault detection using the HVSR method
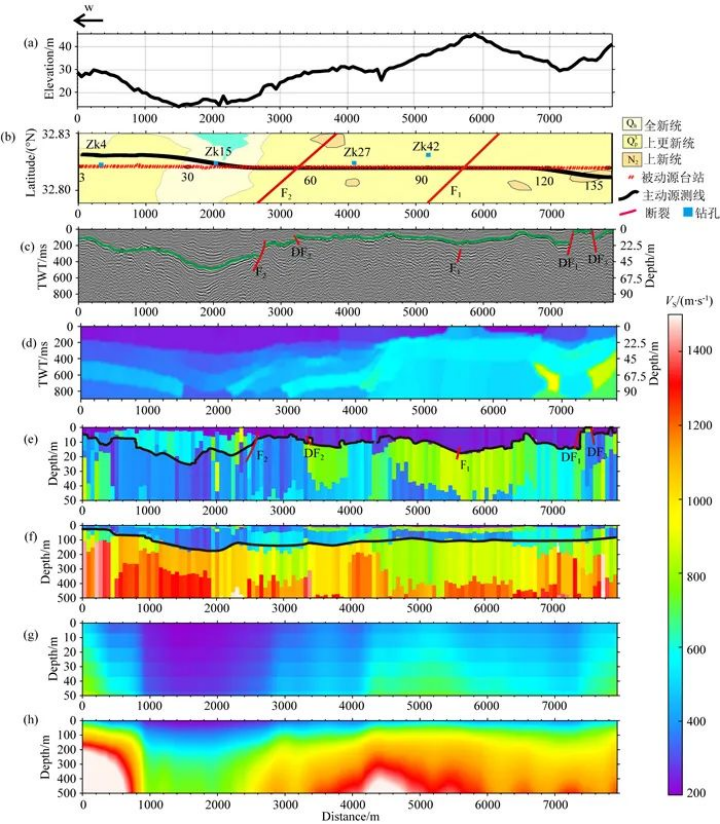
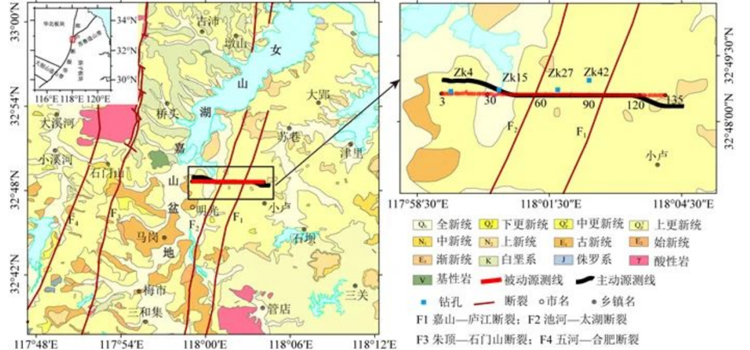
Distribution of 1:250,000 geological formations, active and passive source lines and boreholes in the study area.
The topography of Mingguang area is high in the north and low in the south: plains in the north, hills in the centre, and low mountains in the south; the stratigraphy belongs to two stratigraphic regions, the northwestern part of which is the North China Stratigraphic Region, and the southeastern part of which is the South China Stratigraphic Region. The lithology in the area is complex, and at the same time, it receives a large amount of Quaternary deposits in the low-lying basin area.
The traditional method to carry out the related investigation is costly, shallow in exploration depth and limited in construction. In recent years the background noise surface wave exploration method has gradually become an important means in the shallow surface fine structure exploration research.
In order to obtain the fine site response characteristics of the Mingguang section of the Tantanlu Fault Zone, and at the same time to explore the possibility of applying the noise HVSR method to seismic zoning and active fault detection, the scientists of this project used 133 SmartSolo IGU-16HR 3C three-component node seismometers for background noise data acquisition.
The acquired data were used to calculate the HVSR curves of the profiles and obtain the peak frequency of the profiles, and then the shallow S-wave velocity structure was inverted using the particle swarm algorithm. Finally, the reliability of the method was verified by combining with the peripheral boreholes, the artificial shallow seismic reflection profiles, and the inverted S-wave velocities of the dispersion curves on the same survey line, to further analyse the depositional pattern and the characteristics of the hidden faults, and to explore the geological genesis.
The study draws the following conclusions:
(1) The HVSR profiles below the survey line show complex double-peak and multi-peak patterns, and their site classifications are all Class II medium-hard soils, but the peak frequency varies a lot, and the amplification effect of the western depression area on the strong ground shaking should be paid attention to.
(2)The soil-rock interface revealed by the S-wave velocity structure of HVSR inversion is consistent with the borehole results, and its distribution pattern and trend are highly consistent with the shallow seismic reflection profile results, and the weathered bedrock-unweathered bedrock interface, which the active source fails to depict, is depicted; (3)The soil-rock interface revealed by the S-wave velocity structure of HVSR inversion is consistent with the borehole results, and its distribution pattern and trend is highly consistent with the shallow seismic reflection profile results.
(3)The spatial distribution and activity of the two ruptures at the eastern boundary of the Tantan-Lu Fracture Zone, as depicted by the S-wave velocity structure of HVSR, are consistent with the results of the drilling, shallow seismic, frequency dispersion inversion, and geological tectonics, etc., and reveal that the Chihuhe-Taihu Lake rupture is more active than the Jashan-Lujiang rupture, and may be an active rupture.
The results show that the HVSR method can be applied to urban site response characteristics, shallow sedimentary structure and hidden active fault detection.
Original source: Ni Hongyu, Zhang Ruohan, Li Junlun, Huang Xianliang, Zheng Haigang, Hong Dequan, Miao Peng, Peng Liuya, Bao Ziwen.2023.Application of seismic background noise HVSR method in response characterisation of urban sites and detection of active faults in Mingguang, Anhui Province. Geophysical Journal,66(11):4552-4571,doi:10.6038/cjg2023R0118



