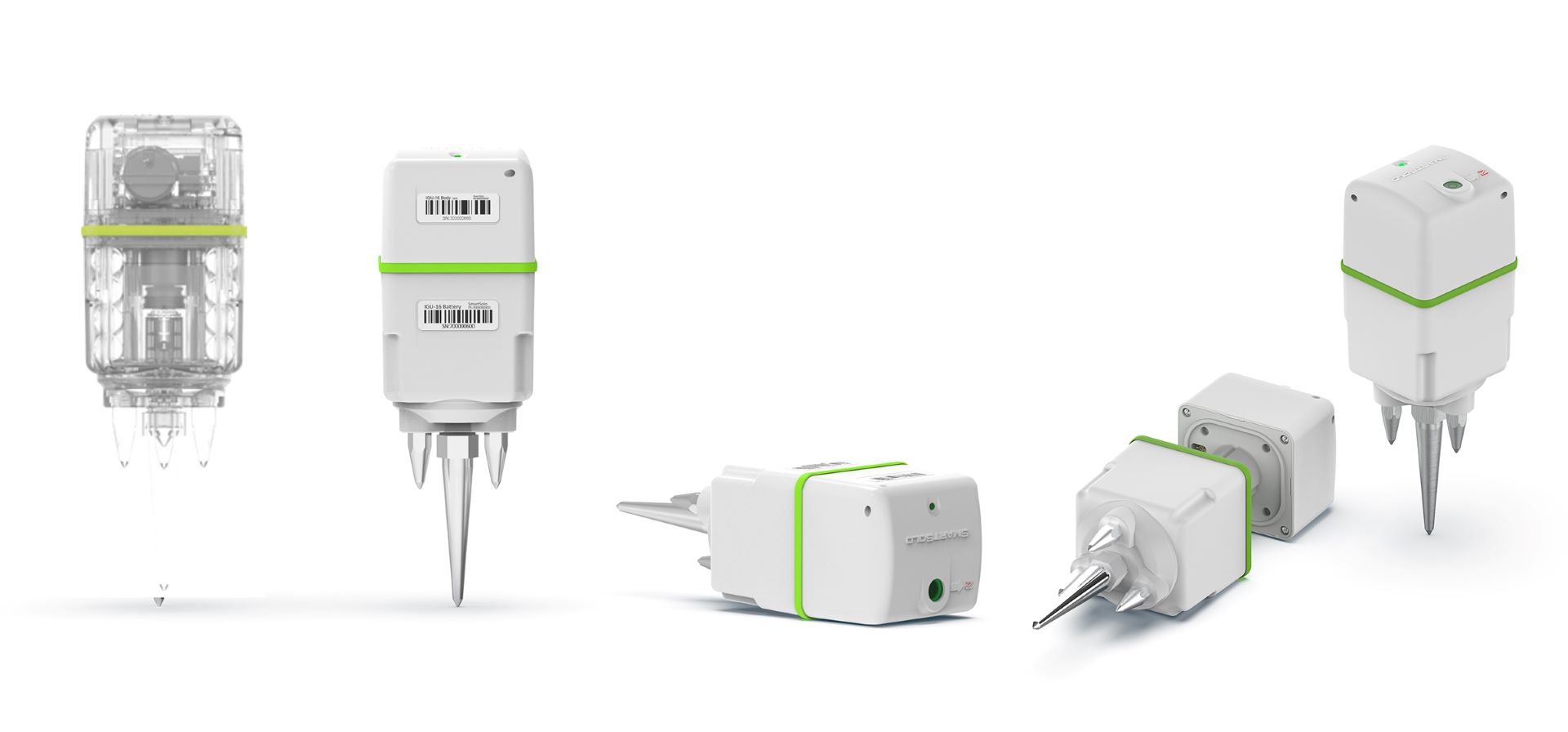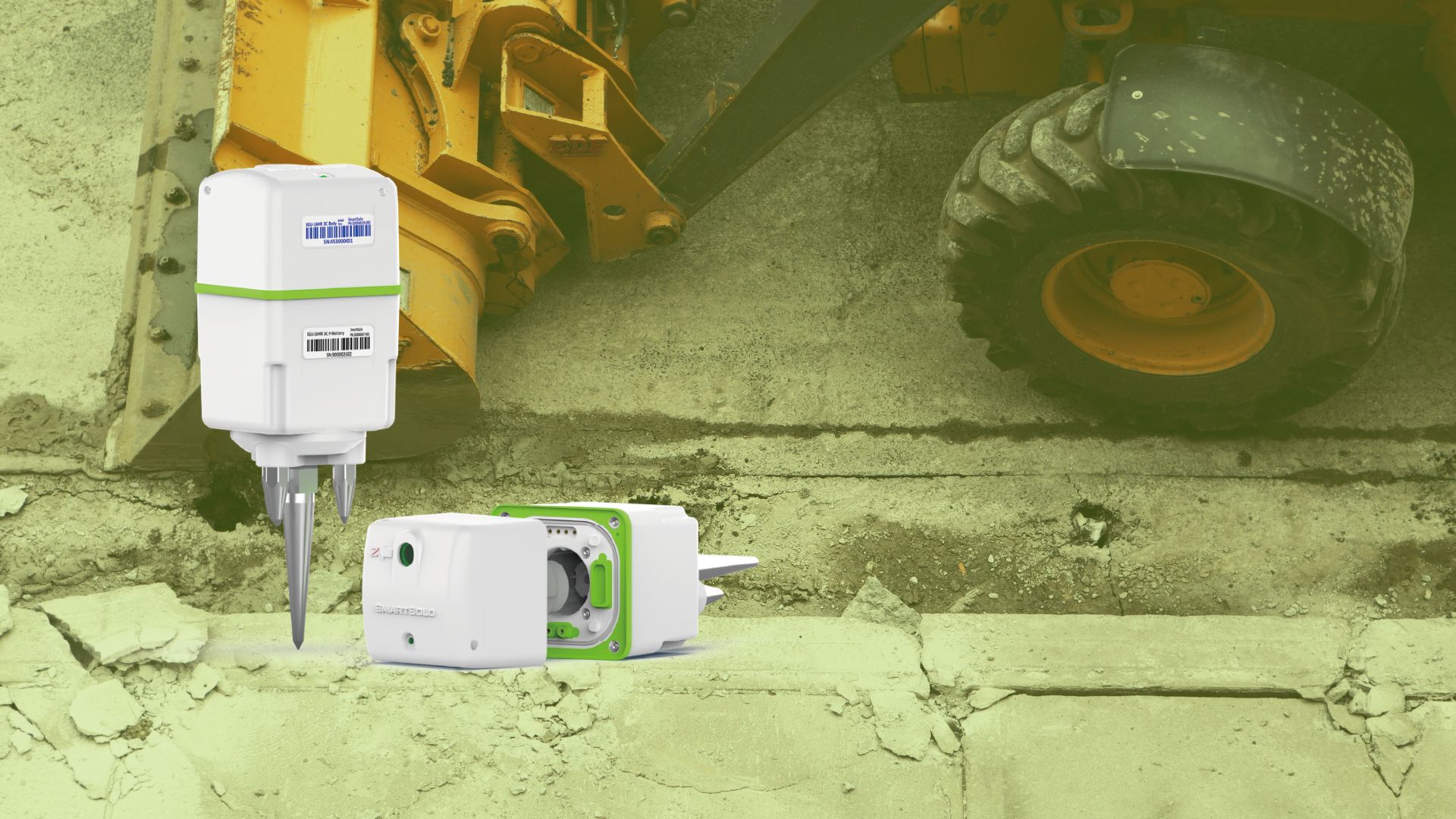
Equipment Model: IGU-16HR 3C
Exploring the Universe in a New Way with the Einstein Telescope
The burgeoning field of gravitational wave astronomy has already revolutionized our understanding of the universe. From detecting the echoes of black hole mergers to witnessing the collision of neutron stars, these ripples in spacetime provide an entirely new way to observe the universe. The Einstein Telescope, a proposed third-generation observatory, aims to push these boundaries even further, offering a sensitivity surpassing its predecessors by a factor of ten.
This unparalleled sensitivity will allow researchers to probe deeper into the universe, capturing faint signals from the earliest epochs of its existence. By listening to these gravitational whispers, the Einstein Telescope will enable us to:
Witness the birth process of black holes and explore their enigmatic nature.
Decipher the structure of neutron stars - these ultra-dense remnants of stellar explosions.
Unravel the mysteries of the universe's first moments - peering back in time closer to the Big Bang than ever before.
Test the predictions of Einstein's theory of relativity with unprecedented precision, potentially revealing new insights into the fundamental laws of physics.
The Quest for Silence: Mitigating Seismic Noise
The success of the Einstein Telescope hinges on its ability to detect the faintest gravitational waves. This requires an environment of extraordinary stillness, shielded from the constant barrage of vibrations that pervade our planet. To achieve this, researchers are focusing on:
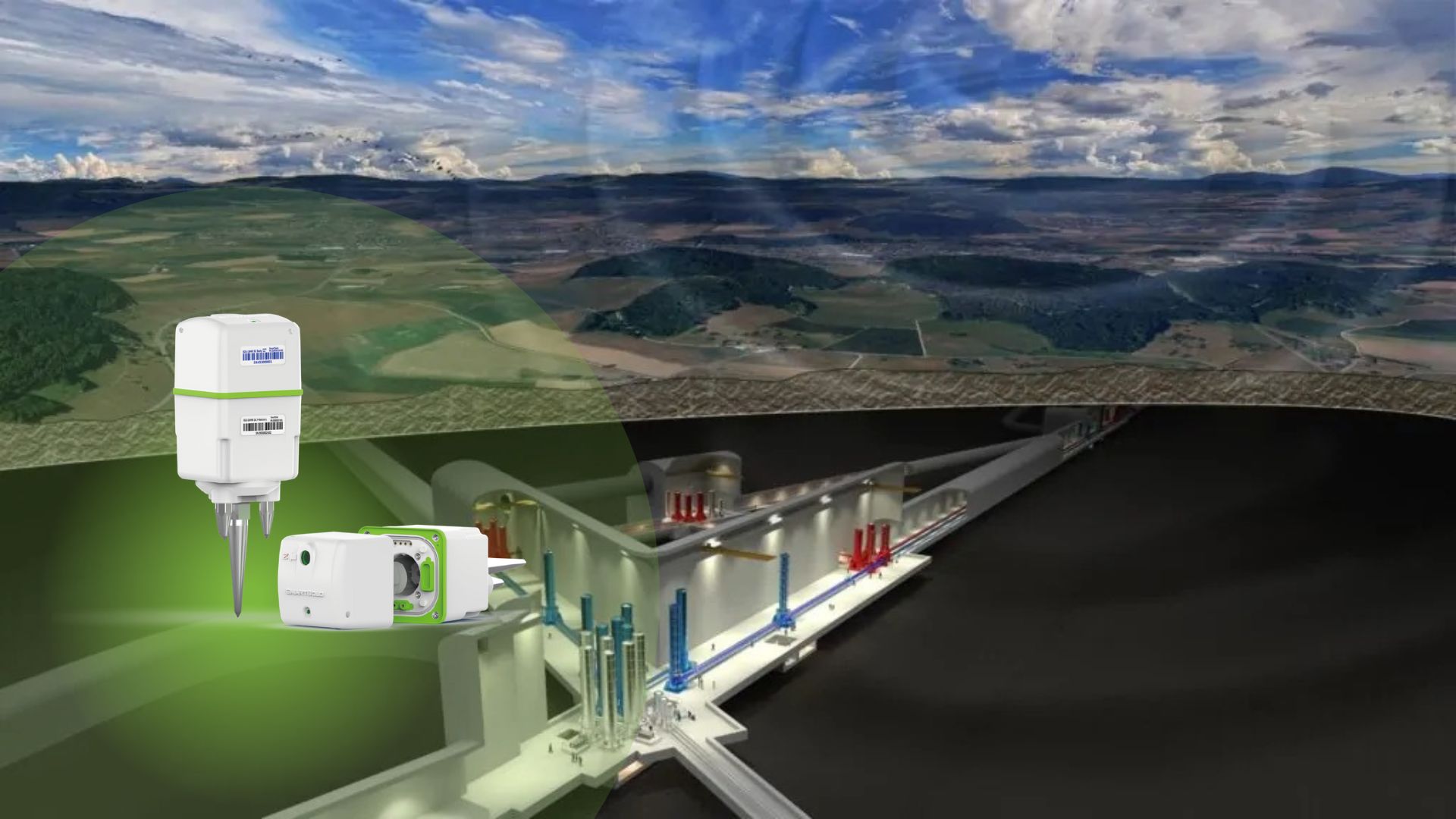
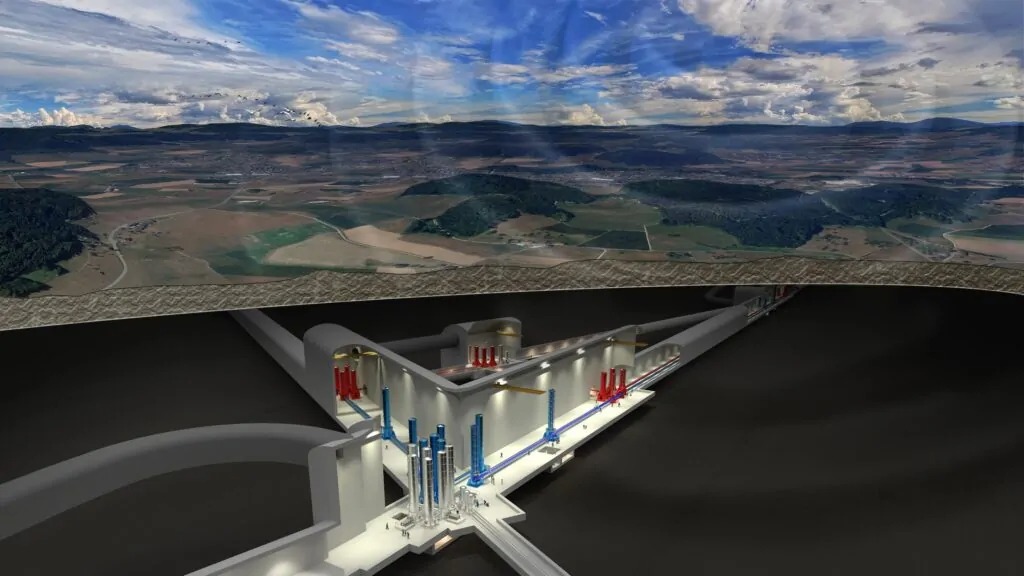
Site Selection: The Einstein Telescope will be built underground, 250 to 300 meters below the surface, providing a first line of defense against surface vibrations. The border region of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Germany, with its unique soft topsoil that naturally dampens vibrations, has emerged as a promising location.
Vibration Isolation: Sophisticated vibration isolation systems will be employed to shield the telescope's sensitive detectors from any remaining ground motion.
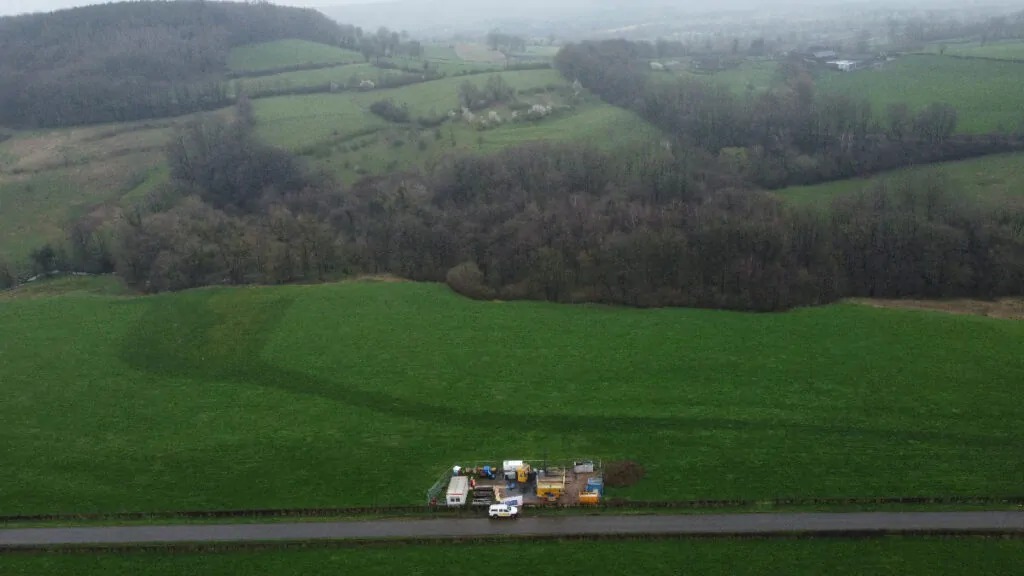

SmartSolo Nodes: Mapping the Seismic Landscape
To ensure optimal sensitivity and to guide the development of effective vibration mitigation strategies, a detailed understanding of the site's seismic environment is paramount. This is where the SmartSolo IGU-16HR 3C nodes come into play.
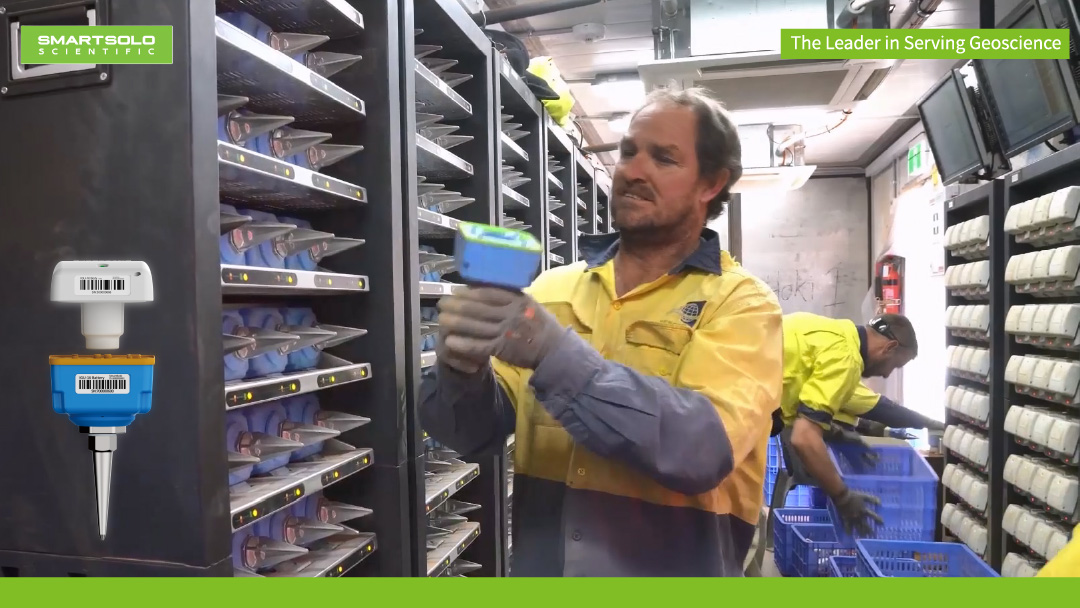
In a project involving 250 nodes, researchers are conducting a comprehensive "passive seismicity" study across the proposed site. These compact nodes are buried and left to passively record ground vibrations for three to four weeks. This meticulous survey will offer valuable insights into the seismic landscape of the site.
We dig a small hole to place the geophones at a depth of around 15 centimeters. After three or four weeks, we retrieve them and close up the hole properly. You don’t notice much.
——Dr. Hadrien Michel, researcher at the University of Liège.
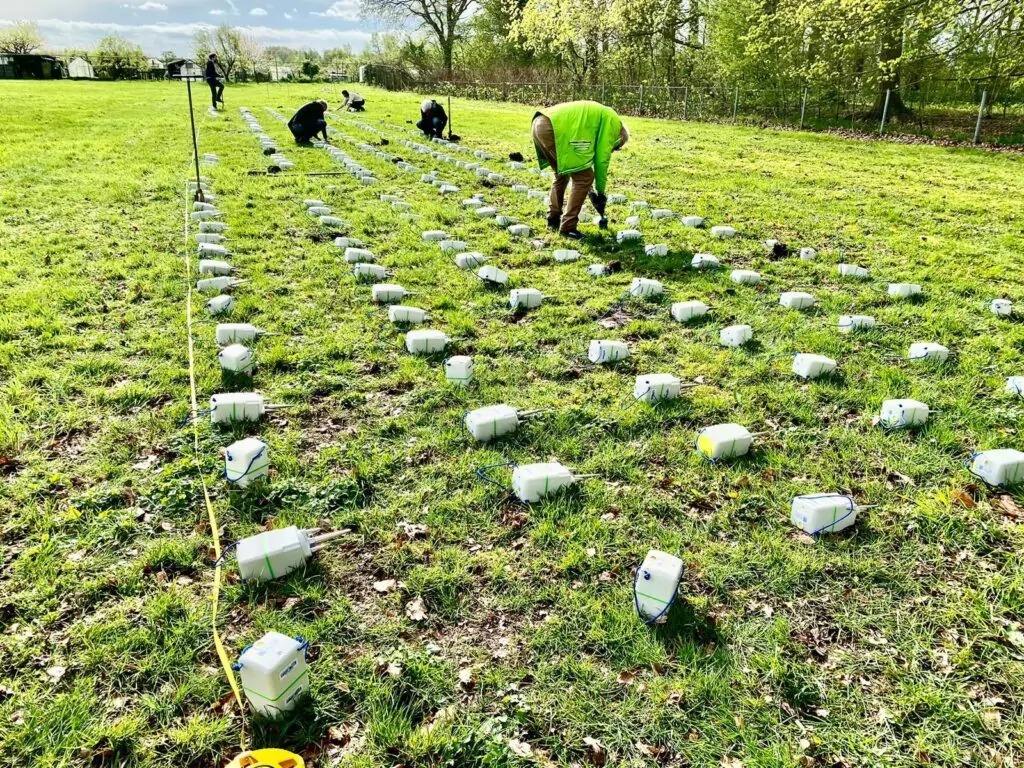

The Advantages of the SmartSolo IGU-16HR 3C Nodes:
These nodes offer several key advantages that make them ideally suited for this critical task:
Three-Component Sensors: The IGU-16HR 3C nodes capture ground motion across all three spatial dimensions (x, y, and z), providing a holistic view of the seismic environment. This detailed data is essential for identifying the direction of vibration propagation and pinpointing the sources of noise.
High Sensitivity: SmartSolo nodes are engineered to detect even the subtlest of ground vibrations, ensuring that the survey captures a complete representation of the site's seismic activity. This level of sensitivity is crucial for identifying potential sources of interference that could compromise the Einstein Telescope's ability to detect faint gravitational waves.
Ease of Deployment: The compact and self-contained design of the node allows for rapid and minimally disruptive deployment and retrieval, optimizing the survey process and minimizing any environmental disturbance.

Analyzing the Data: Uncovering the Sources of Seismic Noise
The data collected by the SmartSolo nodes will be meticulously analyzed by seismologists collaborating with the Einstein Telescope project. This analysis will provide a nuanced understanding of the various types and sources of seismic noise present at the site, including:
Natural Sources: Earthquakes, wind, ocean waves, and even the flow of rivers can generate seismic waves that propagate through the Earth's crust. Understanding the patterns and intensity of these natural sources is crucial for assessing their potential impact on the Einstein Telescope.
Anthropogenic Sources: Human activities, such as road traffic, construction, industrial processes, and even agricultural practices, can generate significant levels of seismic noise. The survey will identify the prevalence and characteristics of these sources, enabling researchers to develop strategies to minimize their impact on the telescope.
Insights fr-om the Seismic Survey
The insights gleaned fr-om this comprehensive seismic survey will play a critical role in shaping the design, construction, and operation of the Einstein Telescope:
Vibration Isolation: The findings will inform the development of advanced vibration isolation systems tailored to mitigate the specific types of seismic noise identified at the site. These systems will act as a shield, protecting the telescope's sensitive detectors fr-om ground vibrations.
Site Layout: The data will help determine the optimal placement of key infrastructure components, such as the telescope's detectors and supporting infrastructure, to minimize their exposure to specific sources of seismic noise. This strategic positioning will further enhance the telescope's ability to detect faint gravitational waves.
Operational Strategies: Understanding the temporal patterns of seismic noise will enable researchers to develop operational strategies to minimize its impact. For example, observations could be scheduled during periods of lower seismic activity or data processing techniques could be employed to filter out specific types of noise.
SmartSolo: Contributing to a Groundbreaking Endeavor
The Einstein Telescope represents a monumental step forward in our quest to understand the universe. It promises to unveil the secrets of some of the most extreme and enigmatic objects in the universe, providing unprecedented insights into the fundamental laws of physics. SmartSolo is proud to contribute its cutting-edge seismic solutions to this groundbreaking endeavor. The IGU-16HR 3C nodes play a vital role in characterizing the site's environment, ensuring the telescope can remain at its highest sensitivity level, and maximizing its potential for groundbreaking discoveries.
SmartSolo Scientific is a pioneer in engineering cutting edge technology to serve the scientific community and aim to make geophysical exploration more accessible and impactful.




