Equipment Model: SmartSolo IGU-16HR 3C
Number of units: 200
Research Overview:
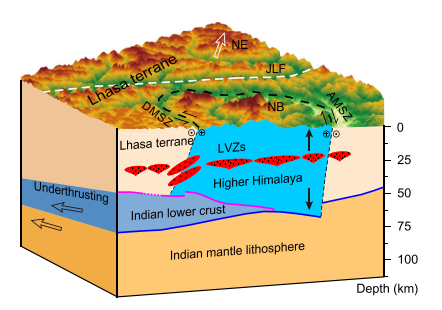
The answer to the question of how the crust deforms in the tectonics of the eastern Himalayas during the collision of the Indian and Asian plates is still unclear. Here we show for the first time high-resolution receiver function images of crustal structures along a new NW-SE-trending dense array of stations crossing the Himalayan tectonic belt. We observe two sets of low-velocity zones, one below the western part of the Lhasa Massif and the High Himalayan region at a depth of 18 ~ 20 km, which is flat; and the other below the western part of the Yarlung Tsangpo Suture Belt at a depth of 10 ~ 30 km, which is two westward-trending types. These low-velocity zones caused by partially molten and aqueous fluids are separated from each other and impede the formation of crustal flows. Under the Ankiga-Motoro shear zone, an eastward-dipping internal crustal discontinuity and a pronounced Moho dislocation with a length of 7 Km are identified, suggesting that retrogression of the subducting crust beneath the Indian Plate and a pure shear mechanism together dominate crustal deformation in the Eastern Himalayan tectonic belt.
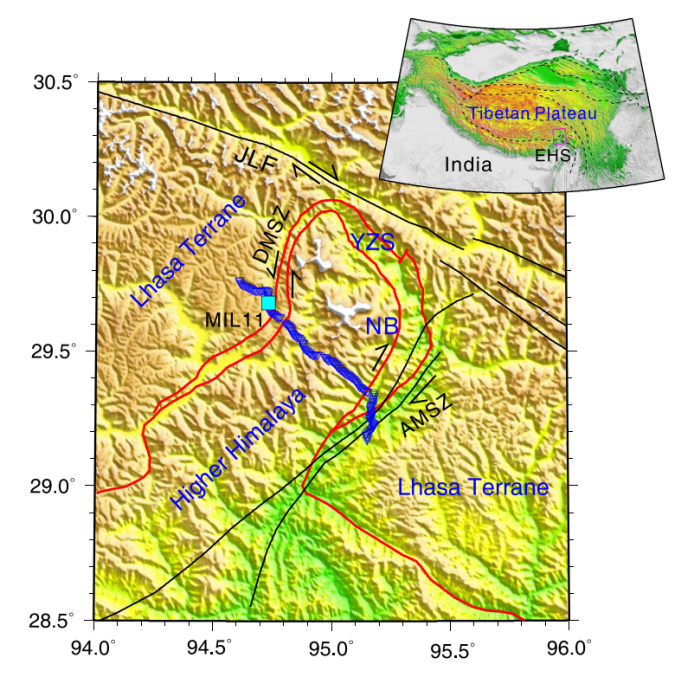
Blue inverted triangles are dense stations consisting of 200 IGU-16HR 3Cs
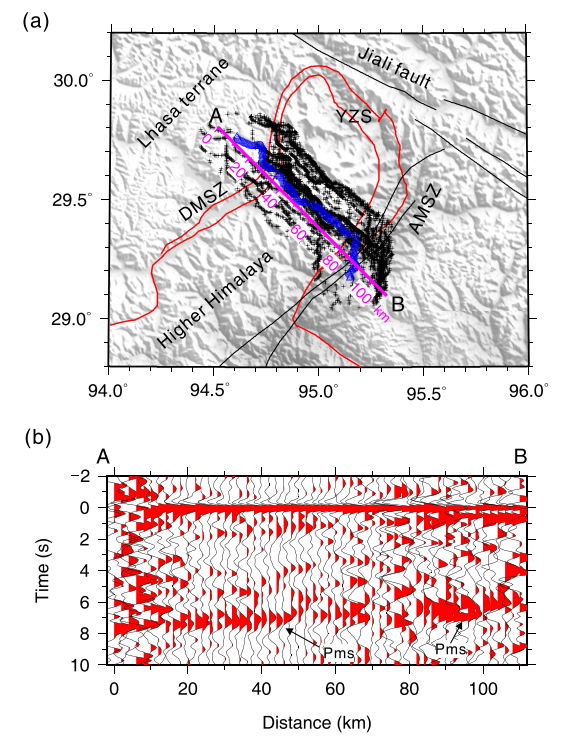
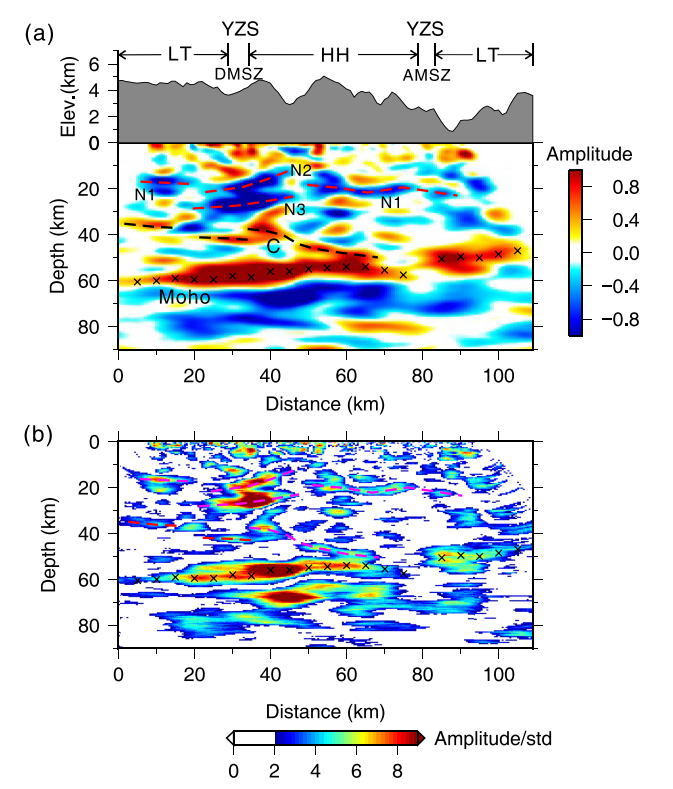
The SmartSolo IGU-16HR 3C Seismic Equipment is a sophisticated tool designed for conducting high-resolution imaging of subsurface structures and seismic events. In a recent case study, this advanced equipment was utilized to assess and analyze the dominant mechanisms driving crustal deformation within the Himalayan tectonic junction located on the eastern Tibetan Plateau.
Through the application of Receiver Function Imaging techniques, the SmartSolo IGU-16HR 3C Seismic Equipment enabled researchers to obtain detailed insights into the geological processes shaping the Earth's crust in this specific region. The study focused on estimating the prevalence of two primary mechanisms contributing to crustal deformation: backwash and pure shear.
Backwash mechanisms involve the movement of materials in response to gravitational forces, leading to vertical uplift or subsidence of the Earth's surface. Pure shear mechanisms, on the other hand, result from parallel forces acting in opposite directions, causing horizontal stretching or compressing of the crust.
By accurately estimating the dominance of these mechanisms, the SmartSolo IGU-16HR 3C Seismic Equipment played a crucial role in enhancing our understanding of tectonic dynamics in the Himalayan region. The findings from this study provide valuable insights into the complex geological processes occurring at the tectonic junction on the eastern Tibetan Plateau, contributing to advancements in seismic research and geological exploration.



