In recent years, earthquakes are frequent and disasters are relentless, and life is so fragile in front of earthquakes. Scholars at home and abroad have been paying close attention to the deep-seismogenic environment and potential seismic hazards in earthquake-prone regions in the hope that scientific guidance can be given to infrastructure construction as well as disaster prevention and mitigation through the study of geological structures in earthquake-prone regions.
The following is the continuous waveform data of the 6.0 magnitude earthquake that occurred in Lu County, Luzhou City, Sichuan Province, on 16 September 2021, recorded by the Geodynamics Laboratory of the Chengdu Tibetan Plateau Seismological Research Institute of the China Earthquake Administration (CTSA) using a short-period, dense seismic observatory array deployed by a SmartSolo smart node seismometer, and the three-dimensional S-wave velocity structure of the seismic region constructed using the background noise imaging method, to analyse and study the velocity structure characteristics, seismic distribution characteristics, and velocity structure and seismic distribution characteristics of the Lu County earthquake region. The study analyses and researches the structural characteristics, seismic distribution characteristics, and deep seismic background of the LuXian earthquake area.
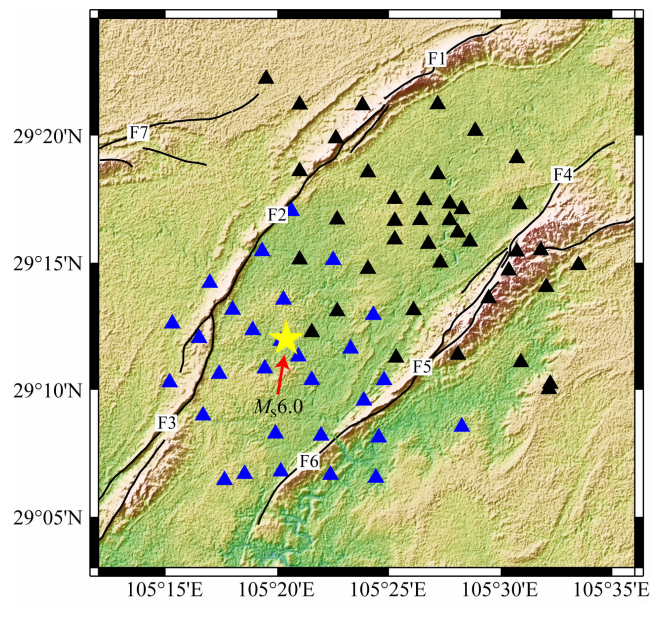
The Chengdu Tibetan Plateau Seismological Research Institute (CPTSRI) of the China Earthquake Administration (CEA) has set up a total of 70 sets of dense short-period seismic observation stations (with an average spacing of 2-3km and a raw data sampling rate of 10ms) in the Luxian seismic area and its vicinity, and has completed the seismic array setup tasks in two batches. The first batch was set up before the Lu County earthquake on 16 September 2021, 40 seismic stations (black triangles) were set up in the north-east of the epicentre, and the continuous waveforms were recorded from 10 September 2021 to 22 October 2021, which successfully captured the 6.0 mainshock and a large number of aftershocks in Lu County.
The second batch of 30 short-period seismic instruments (blue triangles) were deployed southwest of the epicentre of the Lu County 6.0 earthquake on 16 September 2021 for intensive monitoring of the earthquake situation and tectonic analysis of the pregnant earthquake, and the continuous waveforms were recorded from 23 September 2021 to 22 October 2021, and the second batch of 30 short-period seismic instruments (blue triangles) were deployed southwest of the epicentre of the earthquake.
After processing the acquired seismic data and Rayleigh wave inversion, the study obtained good results:
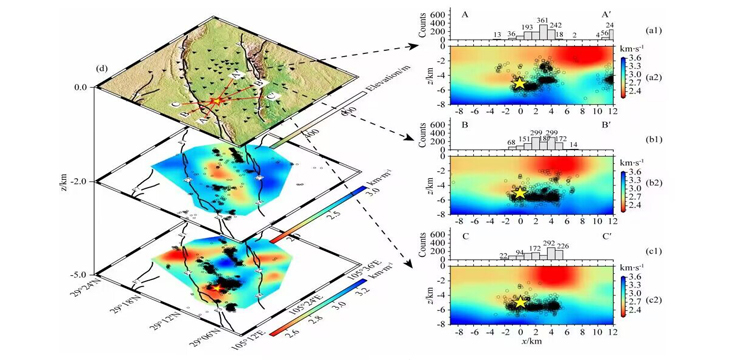
The research results provide guidance and basis for understanding the causal mechanism and dynamic background of the 6.0 magnitude earthquake in Lu County, scientifically investigating the trend of seismic activity in the region and accurately evaluating potential seismic hazards, as well as mitigating the risk of seismic hazards as much as possible, and to a certain extent, make up for the lack of high-resolution, deep, and fine geophysical data in the area near the epicentre of the earthquake in Lu County over a long period of time.
Scientists have never stopped exploring the earth, trying new ways to understand the earth in more detail, and providing scientific guidance to reduce the losses caused by earthquake disasters. It is believed that in the near future, science will open more scientific doors for us to reveal the mysteries of the earth and create a safer, greener and better future for us.
References "Three-dimensional s-wave fine velocity structure in the earthquake zone of the 16 September 2021 Sichuan Luxian Ms6.0 earthquake



