SmartSolo Node Seismographs Provide Robust and Reliable Equipment for SEG's "Characterization of Environmental Seismic Noise" Survey Project
SEG researchers deployed a patch of 64 SmartSolo IGU-16 1C seismic nodes in South Central South Dakota to characterize the ambient seismic noise in the area The nodes were deployed on a 100-meter grid and recorded continuously for 7 days without any issues. The deployment of the nodes took only 3 hours, demonstrating high operational efficiency. The objective of this survey was to characterize the ambient seismic noise in the area to advise as to the robustness of passive methods to de-risk future projects. The data results of this project demonstrate that passive data can significantly enhance the derived model of shear wave velocity (MASW) for studying deeper layers, as the available spectrum's lower limit extends from 5.5 Hz (active data) to approximately 2.5 Hz (passive data).
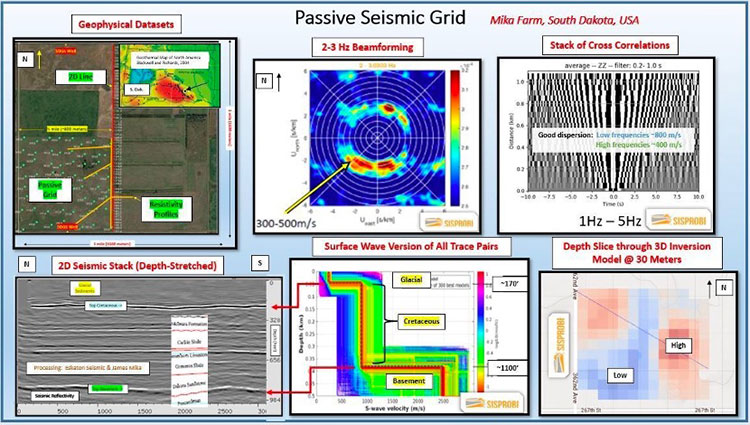
A few pertinent observations include (refer to montage, below):
Beamforming suggests a fairly isotropic distribution of signal (top center), over a frequency range of 1-5 hertz. Noise (ambient signal) sources include road traffic and potentially the Missouri River, situated a few miles to the south/west.
The stack of the cross correlations (top right) exhibits good dispersion, suggesting a robust derivation of a surface wave model (Vs (shear wave)) is possible.
The 1D Vs model (bottom center) describes a 3 layer model, which agrees well with depths to the top of bedrock and basement, as known from well control and the 2D active stacked section (bottom left)
The 3D depth inversion result (lower right) possesses velocity anomalies in the glacial section that correlate well with topographic (and seismic) expressions of a buried glacial valley system.
Results indicate passive data could contribute significantly to subsurface characterization.
Article source: Society of Exploration Geophysicists (SEG) James Mika
https://lnkd.in/gpqWddeg
Nodes and data harvesting were provided by Seismic Equipment Specialists, LLC (Ross Kennedy & Boyse Harris).



